kwcoco.util.delayed_ops package¶
Submodules¶
Module contents¶
Functionality has been ported to delayed_image
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedArray(subdata=None)[source]¶
Bases:
DelayedUnaryOperationA generic NDArray.
- property shape¶
Returns: None | Tuple[int | None, …]
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedAsXarray(subdata=None, dsize=None, channels=None)[source]¶
Bases:
DelayedImageCasts the data to an xarray object in the finalize step
- Example;
>>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(module:xarray) >>> from delayed_image.delayed_nodes import * # NOQA >>> from delayed_image import DelayedLoad >>> # without channels >>> base = DelayedLoad.demo(dsize=(16, 16)).prepare() >>> self = base.as_xarray() >>> final = self._validate().finalize() >>> assert len(final.coords) == 0 >>> assert final.dims == ('y', 'x', 'c') >>> # with channels >>> base = DelayedLoad.demo(dsize=(16, 16), channels='r|g|b').prepare() >>> self = base.as_xarray() >>> final = self._validate().finalize() >>> assert final.coords.indexes['c'].tolist() == ['r', 'g', 'b'] >>> assert final.dims == ('y', 'x', 'c')
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedChannelConcat(parts, dsize=None)[source]¶
Bases:
ImageOpsMixin,DelayedConcatStacks multiple arrays together.
Example
>>> from delayed_image import * # NOQA >>> from delayed_image.delayed_leafs import DelayedLoad >>> dsize = (307, 311) >>> c1 = DelayedNans(dsize=dsize, channels='foo') >>> c2 = DelayedLoad.demo('astro', dsize=dsize, channels='R|G|B').prepare() >>> cat = DelayedChannelConcat([c1, c2]) >>> warped_cat = cat.warp({'scale': 1.07}, dsize=(328, 332)) >>> warped_cat._validate() >>> warped_cat.finalize()
Example
>>> # Test case that failed in initial implementation >>> # Due to incorrectly pushing channel selection under the concat >>> from delayed_image import * # NOQA >>> import kwimage >>> fpath = kwimage.grab_test_image_fpath() >>> base1 = DelayedLoad(fpath, channels='r|g|b').prepare() >>> base2 = DelayedLoad(fpath, channels='x|y|z').prepare().scale(2) >>> base3 = DelayedLoad(fpath, channels='i|j|k').prepare().scale(2) >>> bands = [base2, base1[:, :, 0].scale(2).evaluate(), >>> base1[:, :, 1].evaluate().scale(2), >>> base1[:, :, 2].evaluate().scale(2), base3] >>> delayed = DelayedChannelConcat(bands) >>> delayed = delayed.warp({'scale': 2}) >>> delayed = delayed[0:100, 0:55, [0, 2, 4]] >>> delayed.write_network_text() >>> delayed.optimize()
- property channels¶
Returns: None | FusedChannelSpec
- property shape¶
Returns: Tuple[int | None, int | None, int | None]
- take_channels(channels)[source]¶
This method returns a subset of the vision data with only the specified bands / channels.
- Parameters
channels (List[int] | slice | channel_spec.FusedChannelSpec) – List of integers indexes, a slice, or a channel spec, which is typically a pipe (|) delimited list of channel codes. See
ChannelSpecfor more detials.- Returns
a delayed vision operation that only operates on the following channels.
- Return type
Example
>>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(module:kwcoco) >>> from delayed_image.delayed_nodes import * # NOQA >>> import kwcoco >>> dset = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo('vidshapes8-multispectral') >>> self = delayed = dset.coco_image(1).delay(mode=1) >>> channels = 'B11|B8|B1|B10' >>> new = self.take_channels(channels)
Example
>>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(module:kwcoco) >>> # Complex case >>> import kwcoco >>> from delayed_image.delayed_nodes import * # NOQA >>> from delayed_image.delayed_leafs import DelayedLoad >>> dset = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo('vidshapes8-multispectral') >>> delayed = dset.coco_image(1).delay(mode=1) >>> astro = DelayedLoad.demo('astro', channels='r|g|b').prepare() >>> aligned = astro.warp(kwimage.Affine.scale(600 / 512), dsize='auto') >>> self = combo = DelayedChannelConcat(delayed.parts + [aligned]) >>> channels = 'B1|r|B8|g' >>> new = self.take_channels(channels) >>> new_cropped = new.crop((slice(10, 200), slice(12, 350))) >>> new_opt = new_cropped.optimize() >>> datas = new_opt.finalize() >>> if 1: >>> new_cropped.write_network_text(with_labels='name') >>> new_opt.write_network_text(with_labels='name') >>> vizable = kwimage.normalize_intensity(datas, axis=2) >>> self._validate() >>> new._validate() >>> new_cropped._validate() >>> new_opt._validate() >>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(--show) >>> import kwplot >>> kwplot.autompl() >>> stacked = kwimage.stack_images(vizable.transpose(2, 0, 1)) >>> kwplot.imshow(stacked)
Example
>>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(module:kwcoco) >>> # Test case where requested channel does not exist >>> import kwcoco >>> from delayed_image.delayed_nodes import * # NOQA >>> dset = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo('vidshapes8-multispectral', use_cache=1, verbose=100) >>> self = delayed = dset.coco_image(1).delay(mode=1) >>> channels = 'B1|foobar|bazbiz|B8' >>> new = self.take_channels(channels) >>> new_cropped = new.crop((slice(10, 200), slice(12, 350))) >>> fused = new_cropped.finalize() >>> assert fused.shape == (190, 338, 4) >>> assert np.all(np.isnan(fused[..., 1:3])) >>> assert not np.any(np.isnan(fused[..., 0])) >>> assert not np.any(np.isnan(fused[..., 3]))
- property num_overviews¶
Returns: int
- undo_warps(remove=None, retain=None, squash_nans=False, return_warps=False)[source]¶
Attempts to “undo” warping for each concatenated channel and returns a list of delayed operations that are cropped to the right regions.
Typically you will retrain offset, theta, and shear to remove scale. This ensures the data is spatially aligned up to a scale factor.
- Parameters
remove (List[str]) – if specified, list components of the warping to remove. Can include: “offset”, “scale”, “shearx”, “theta”. Typically set this to [“scale”].
retain (List[str]) – if specified, list components of the warping to retain. Can include: “offset”, “scale”, “shearx”, “theta”. Mutually exclusive with “remove”. If neither remove or retain is specified, retain is set to
[].squash_nans (bool) – if True, pure nan channels are squashed into a 1x1 array as they do not correspond to a real source.
return_warps (bool) – if True, return the transforms we applied. I.e. the transform from the
selfto the returnedparts. This is useful when you need to warp objects in the original space into the jagged space.
- Returns
The List[DelayedImage] are the
partsi.e. the new images with the warping undone. The List[Affine]: is the transforms fromselfto each item inparts- Return type
List[DelayedImage] | Tuple[List[DelayedImage] | List[Affine]]
Example
>>> from delayed_image.delayed_nodes import * # NOQA >>> from delayed_image.delayed_leafs import DelayedLoad >>> from delayed_image.delayed_leafs import DelayedNans >>> import ubelt as ub >>> import kwimage >>> import kwarray >>> import numpy as np >>> # Demo case where we have different channels at different resolutions >>> base = DelayedLoad.demo(channels='r|g|b').prepare().dequantize({'quant_max': 255}) >>> bandR = base[:, :, 0].scale(100 / 512)[:, :-50].evaluate() >>> bandG = base[:, :, 1].scale(300 / 512).warp({'theta': np.pi / 8, 'about': (150, 150)}).evaluate() >>> bandB = base[:, :, 2].scale(600 / 512)[:150, :].evaluate() >>> bandN = DelayedNans((600, 600), channels='N') >>> # Make a concatenation of images of different underlying native resolutions >>> delayed_vidspace = DelayedChannelConcat([ >>> bandR.scale(6, dsize=(600, 600)).optimize(), >>> bandG.warp({'theta': -np.pi / 8, 'about': (150, 150)}).scale(2, dsize=(600, 600)).optimize(), >>> bandB.scale(1, dsize=(600, 600)).optimize(), >>> bandN, >>> ]).warp({'scale': 0.7}).optimize() >>> vidspace_box = kwimage.Boxes([[100, 10, 270, 160]], 'ltrb') >>> vidspace_poly = vidspace_box.to_polygons()[0] >>> vidspace_slice = vidspace_box.to_slices()[0] >>> self = delayed_vidspace[vidspace_slice].optimize() >>> print('--- Aligned --- ') >>> self.write_network_text() >>> squash_nans = True >>> undone_all_parts, tfs1 = self.undo_warps(squash_nans=squash_nans, return_warps=True) >>> undone_scale_parts, tfs2 = self.undo_warps(remove=['scale'], squash_nans=squash_nans, return_warps=True) >>> stackable_aligned = self.finalize().transpose(2, 0, 1) >>> stackable_undone_all = [] >>> stackable_undone_scale = [] >>> print('--- Undone All --- ') >>> for undone in undone_all_parts: ... undone.write_network_text() ... stackable_undone_all.append(undone.finalize()) >>> print('--- Undone Scale --- ') >>> for undone in undone_scale_parts: ... undone.write_network_text() ... stackable_undone_scale.append(undone.finalize()) >>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(--show) >>> import kwplot >>> kwplot.autompl() >>> canvas0 = kwimage.stack_images(stackable_aligned, axis=1) >>> canvas1 = kwimage.stack_images(stackable_undone_all, axis=1) >>> canvas2 = kwimage.stack_images(stackable_undone_scale, axis=1) >>> canvas0 = kwimage.draw_header_text(canvas0, 'Rescaled Aligned Channels') >>> canvas1 = kwimage.draw_header_text(canvas1, 'Unwarped Channels') >>> canvas2 = kwimage.draw_header_text(canvas2, 'Unscaled Channels') >>> canvas = kwimage.stack_images([canvas0, canvas1, canvas2], axis=0) >>> canvas = kwimage.fill_nans_with_checkers(canvas) >>> kwplot.imshow(canvas)

- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedConcat(parts, axis)[source]¶
Bases:
DelayedNaryOperationStacks multiple arrays together.
- property shape¶
Returns: None | Tuple[int | None, …]
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedCrop(subdata, space_slice=None, chan_idxs=None)[source]¶
Bases:
DelayedImageCrops an image along integer pixel coordinates.
Example
>>> from delayed_image.delayed_nodes import * # NOQA >>> from delayed_image import DelayedLoad >>> base = DelayedLoad.demo(dsize=(16, 16)).prepare() >>> # Test Fuse Crops Space Only >>> crop1 = base[4:12, 0:16] >>> self = crop1[2:6, 0:8] >>> opt = self._opt_fuse_crops() >>> self.write_network_text() >>> opt.write_network_text() >>> # >>> # Test Channel Select Via Index >>> self = base[:, :, [0]] >>> self.write_network_text() >>> final = self._finalize() >>> assert final.shape == (16, 16, 1) >>> assert base[:, :, [0, 1]].finalize().shape == (16, 16, 2) >>> assert base[:, :, [2, 0, 1]].finalize().shape == (16, 16, 3)
Example
>>> from delayed_image.delayed_nodes import * # NOQA >>> from delayed_image import DelayedLoad >>> base = DelayedLoad.demo(dsize=(16, 16)).prepare() >>> # Test Discontiguous Channel Select Via Index >>> self = base[:, :, [0, 2]] >>> self.write_network_text() >>> final = self._finalize() >>> assert final.shape == (16, 16, 2)
- optimize()[source]¶
- Returns
DelayedImage
Example
>>> # Test optimize nans >>> from delayed_image import DelayedNans >>> import kwimage >>> base = DelayedNans(dsize=(100, 100), channels='a|b|c') >>> self = base[0:10, 0:5] >>> # Should simply return a new nan generator >>> new = self.optimize() >>> self.write_network_text() >>> new.write_network_text() >>> assert len(new.as_graph().nodes) == 1
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedDequantize(subdata, quantization)[source]¶
Bases:
DelayedImageRescales image intensities from int to floats.
The output is usually between 0 and 1. This also handles transforming nodata into nan values.
- optimize()[source]¶
- Returns
DelayedImage
Example
>>> # Test a case that caused an error in development >>> from delayed_image.delayed_nodes import * # NOQA >>> from delayed_image import DelayedLoad >>> fpath = kwimage.grab_test_image_fpath() >>> base = DelayedLoad(fpath, channels='r|g|b').prepare() >>> quantization = {'quant_max': 255, 'nodata': 0} >>> self = base.get_overview(1).dequantize(quantization) >>> self.write_network_text() >>> opt = self.optimize()
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedFrameStack(parts)[source]¶
Bases:
DelayedStackStacks multiple arrays together.
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedIdentity(data, channels=None, dsize=None)[source]¶
Bases:
DelayedImageLeafReturns an ndarray as-is
Example
self = DelayedNans((10, 10), channel_spec.FusedChannelSpec.coerce(‘rgb’)) region_slices = (slice(5, 10), slice(1, 12)) delayed = self.crop(region_slices)
Example
>>> from delayed_image import * # NOQA >>> arr = kwimage.checkerboard() >>> self = DelayedIdentity(arr, channels='gray') >>> warp = self.warp({'scale': 1.07}) >>> warp.optimize().finalize()
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedImage(subdata=None, dsize=None, channels=None)[source]¶
Bases:
ImageOpsMixin,DelayedArrayFor the case where an array represents a 2D image with multiple channels
- property shape¶
Returns: None | Tuple[int | None, int | None, int | None]
- property num_channels¶
Returns: None | int
- property dsize¶
Returns: None | Tuple[int | None, int | None]
- property channels¶
Returns: None | FusedChannelSpec
- property num_overviews¶
Returns: int
- take_channels(channels)[source]¶
This method returns a subset of the vision data with only the specified bands / channels.
- Parameters
channels (List[int] | slice | channel_spec.FusedChannelSpec) – List of integers indexes, a slice, or a channel spec, which is typically a pipe (|) delimited list of channel codes. See ChannelSpec for more detials.
- Returns
a new delayed load with a fused take channel operation
- Return type
Note
The channel subset must exist here or it will raise an error. A better implementation (via pymbolic) might be able to do better
Example
>>> # >>> # Test Channel Select Via Code >>> from delayed_image.delayed_nodes import * # NOQA >>> from delayed_image import DelayedLoad >>> self = DelayedLoad.demo(dsize=(16, 16), channels='r|g|b').prepare() >>> channels = 'r|b' >>> new = self.take_channels(channels)._validate() >>> new2 = new[:, :, [1, 0]]._validate() >>> new3 = new2[:, :, [1]]._validate()
Example
>>> from delayed_image.delayed_nodes import * # NOQA >>> from delayed_image import DelayedLoad >>> self = DelayedLoad.demo('astro').prepare() >>> channels = [2, 0] >>> new = self.take_channels(channels) >>> new3 = new.take_channels([1, 0]) >>> new._validate() >>> new3._validate()
>>> final1 = self.finalize() >>> final2 = new.finalize() >>> final3 = new3.finalize() >>> assert np.all(final1[..., 2] == final2[..., 0]) >>> assert np.all(final1[..., 0] == final2[..., 1]) >>> assert final2.shape[2] == 2
>>> assert np.all(final1[..., 2] == final3[..., 1]) >>> assert np.all(final1[..., 0] == final3[..., 0]) >>> assert final3.shape[2] == 2
Example
>>> from delayed_image.delayed_nodes import * # NOQA >>> from delayed_image import DelayedLoad >>> self = DelayedLoad.demo(dsize=(16, 16), channels='r|g|b').prepare() >>> # Case where a channel doesn't exist >>> channels = 'r|b|magic' >>> new = self.take_channels(channels) >>> assert len(new.parts) == 2 >>> new._validate()
- undo_warp(remove=None, retain=None, squash_nans=False, return_warp=False)[source]¶
Attempts to “undo” warping for each concatenated channel and returns a list of delayed operations that are cropped to the right regions.
Typically you will retrain offset, theta, and shear to remove scale. This ensures the data is spatially aligned up to a scale factor.
- Parameters
remove (List[str]) – if specified, list components of the warping to remove. Can include: “offset”, “scale”, “shearx”, “theta”. Typically set this to [“scale”].
retain (List[str]) – if specified, list components of the warping to retain. Can include: “offset”, “scale”, “shearx”, “theta”. Mutually exclusive with “remove”. If neither remove or retain is specified, retain is set to
[].squash_nans (bool) – if True, pure nan channels are squashed into a 1x1 array as they do not correspond to a real source.
return_warp (bool) – if True, return the transform we applied. This is useful when you need to warp objects in the original space into the jagged space.
- SeeAlso:
DelayedChannelConcat.undo_warps
Example
>>> # Test similar to undo_warps, but on each channel separately >>> from delayed_image.delayed_nodes import * # NOQA >>> from delayed_image.delayed_leafs import DelayedLoad >>> from delayed_image.delayed_leafs import DelayedNans >>> import ubelt as ub >>> import kwimage >>> import kwarray >>> import numpy as np >>> # Demo case where we have different channels at different resolutions >>> base = DelayedLoad.demo(channels='r|g|b').prepare().dequantize({'quant_max': 255}) >>> bandR = base[:, :, 0].scale(100 / 512)[:, :-50].evaluate() >>> bandG = base[:, :, 1].scale(300 / 512).warp({'theta': np.pi / 8, 'about': (150, 150)}).evaluate() >>> bandB = base[:, :, 2].scale(600 / 512)[:150, :].evaluate() >>> bandN = DelayedNans((600, 600), channels='N') >>> B0 = bandR.scale(6, dsize=(600, 600)).optimize() >>> B1 = bandG.warp({'theta': -np.pi / 8, 'about': (150, 150)}).scale(2, dsize=(600, 600)).optimize() >>> B2 = bandB.scale(1, dsize=(600, 600)).optimize() >>> vidspace_box = kwimage.Boxes([[-10, -10, 270, 160]], 'ltrb').scale(1 / .7).quantize() >>> vidspace_poly = vidspace_box.to_polygons()[0] >>> vidspace_slice = vidspace_box.to_slices()[0] >>> # Test with the padded crop >>> self0 = B0.crop(vidspace_slice, wrap=0, clip=0, pad=10).optimize() >>> self1 = B1.crop(vidspace_slice, wrap=0, clip=0, pad=10).optimize() >>> self2 = B2.crop(vidspace_slice, wrap=0, clip=0, pad=10).optimize() >>> parts = [self0, self1, self2] >>> # Run the undo on each channel >>> undone_scale_parts = [d.undo_warp(remove=['scale']) for d in parts] >>> print('--- Aligned --- ') >>> stackable_aligned = [] >>> for d in parts: >>> d.write_network_text() >>> stackable_aligned.append(d.finalize()) >>> print('--- Undone Scale --- ') >>> stackable_undone_scale = [] >>> for undone in undone_scale_parts: ... undone.write_network_text() ... stackable_undone_scale.append(undone.finalize()) >>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(--show) >>> import kwplot >>> kwplot.autompl() >>> canvas0 = kwimage.stack_images(stackable_aligned, axis=1, pad=5, bg_value='kw_darkgray') >>> canvas2 = kwimage.stack_images(stackable_undone_scale, axis=1, pad=5, bg_value='kw_darkgray') >>> canvas0 = kwimage.draw_header_text(canvas0, 'Rescaled Channels') >>> canvas2 = kwimage.draw_header_text(canvas2, 'Native Scale Channels') >>> canvas = kwimage.stack_images([canvas0, canvas2], axis=0, bg_value='kw_darkgray') >>> canvas = kwimage.fill_nans_with_checkers(canvas) >>> kwplot.imshow(canvas)

- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedImageLeaf(subdata=None, dsize=None, channels=None)[source]¶
Bases:
DelayedImage
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedLoad(fpath, channels=None, dsize=None, nodata_method=None)[source]¶
Bases:
DelayedImageLeafReads an image from disk.
If a gdal backend is available, and the underlying image is in the appropriate formate (e.g. COG) this will return a lazy reference that enables fast overviews and crops.
Example
>>> from delayed_image import * # NOQA >>> self = DelayedLoad.demo(dsize=(16, 16)).prepare() >>> data1 = self.finalize()
Example
>>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(module:osgeo) >>> # Demo code to develop support for overviews >>> from delayed_image import * # NOQA >>> import kwimage >>> import ubelt as ub >>> fpath = kwimage.grab_test_image_fpath(overviews=3) >>> self = DelayedLoad(fpath, channels='r|g|b').prepare() >>> print(f'self={self}') >>> print('self.meta = {}'.format(ub.repr2(self.meta, nl=1))) >>> quantization = { >>> 'quant_max': 255, >>> 'nodata': 0, >>> } >>> node0 = self >>> node1 = node0.get_overview(2) >>> node2 = node1[13:900, 11:700] >>> node3 = node2.dequantize(quantization) >>> node4 = node3.warp({'scale': 0.05}) >>> # >>> data0 = node0._validate().finalize() >>> data1 = node1._validate().finalize() >>> data2 = node2._validate().finalize() >>> data3 = node3._validate().finalize() >>> data4 = node4._validate().finalize() >>> node4.write_network_text()
Example
>>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(module:osgeo) >>> # Test delayed ops with int16 and nodata values >>> from delayed_image import * # NOQA >>> import kwimage >>> from delayed_image.helpers import quantize_float01 >>> import ubelt as ub >>> dpath = ub.Path.appdir('delayed_image/tests/test_delay_nodata').ensuredir() >>> fpath = dpath / 'data.tif' >>> data = kwimage.ensure_float01(kwimage.grab_test_image()) >>> poly = kwimage.Polygon.random(rng=321032).scale(data.shape[0]) >>> poly.fill(data, np.nan) >>> data_uint16, quantization = quantize_float01(data) >>> nodata = quantization['nodata'] >>> kwimage.imwrite(fpath, data_uint16, nodata=nodata, backend='gdal', overviews=3) >>> # Test loading the data >>> self = DelayedLoad(fpath, channels='r|g|b', nodata_method='float').prepare() >>> node0 = self >>> node1 = node0.dequantize(quantization) >>> node2 = node1.warp({'scale': 0.51}, interpolation='lanczos') >>> node3 = node2[13:900, 11:700] >>> node4 = node3.warp({'scale': 0.9}, interpolation='lanczos') >>> node4.write_network_text() >>> node5 = node4.optimize() >>> node5.write_network_text() >>> node6 = node5.warp({'scale': 8}, interpolation='lanczos').optimize() >>> node6.write_network_text() >>> # >>> data0 = node0._validate().finalize() >>> data1 = node1._validate().finalize() >>> data2 = node2._validate().finalize() >>> data3 = node3._validate().finalize() >>> data4 = node4._validate().finalize() >>> data5 = node5._validate().finalize() >>> data6 = node6._validate().finalize() >>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(--show) >>> import kwplot >>> kwplot.autompl() >>> stack1 = kwimage.stack_images([data1, data2, data3, data4, data5]) >>> stack2 = kwimage.stack_images([stack1, data6], axis=1) >>> kwplot.imshow(stack2)
- property fpath¶
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedNans(dsize=None, channels=None)[source]¶
Bases:
DelayedImageLeafConstructs nan channels as needed
Example
self = DelayedNans((10, 10), channel_spec.FusedChannelSpec.coerce(‘rgb’)) region_slices = (slice(5, 10), slice(1, 12)) delayed = self.crop(region_slices)
Example
>>> from delayed_image import * # NOQA >>> dsize = (307, 311) >>> c1 = DelayedNans(dsize=dsize, channels='foo') >>> c2 = DelayedLoad.demo('astro', dsize=dsize, channels='R|G|B').prepare() >>> cat = DelayedChannelConcat([c1, c2]) >>> warped_cat = cat.warp({'scale': 1.07}, dsize=(328, 332))._validate() >>> warped_cat._validate().optimize().finalize()
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedNaryOperation(parts)[source]¶
Bases:
DelayedOperationFor operations that have multiple input arrays
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedOperation[source]¶
Bases:
NiceRepr- as_graph()[source]¶
Builds the underlying graph structure as a networkx graph with human readable labels.
- Returns
networkx.DiGraph
- property shape¶
Returns: None | Tuple[int | None, …]
- prepare()[source]¶
If metadata is missing, perform minimal IO operations in order to prepopulate metadata that could help us better optimize the operation tree.
- Returns
DelayedOperation2
- finalize(prepare=True, optimize=True, **kwargs)[source]¶
Evaluate the operation tree in full.
- Parameters
prepare (bool) – ensure prepare is called to ensure metadata exists if possible before optimizing. Defaults to True.
optimize (bool) – ensure the graph is optimized before loading. Default to True.
**kwargs – for backwards compatibility, these will allow for in-place modification of select nested parameters.
- Returns
ArrayLike
Notes
Do not overload this method. Overload
DelayedOperation2._finalize()instead.
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedOverview(subdata, overview)[source]¶
Bases:
DelayedImageDownsamples an image by a factor of two.
If the underlying image being loaded has precomputed overviews it simply loads these instead of downsampling the original image, which is more efficient.
Example
>>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(module:osgeo) >>> # Make a complex chain of operations and optimize it >>> from delayed_image import * # NOQA >>> import kwimage >>> fpath = kwimage.grab_test_image_fpath(overviews=3) >>> dimg = DelayedLoad(fpath, channels='r|g|b').prepare() >>> dimg = dimg.get_overview(1) >>> dimg = dimg.get_overview(1) >>> dimg = dimg.get_overview(1) >>> dopt = dimg.optimize() >>> if 1: >>> import networkx as nx >>> dimg.write_network_text() >>> dopt.write_network_text() >>> print(ub.repr2(dopt.nesting(), nl=-1, sort=0)) >>> final0 = dimg._finalize()[:] >>> final1 = dopt._finalize()[:] >>> assert final0.shape == final1.shape >>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(--show) >>> import kwplot >>> kwplot.autompl() >>> kwplot.imshow(final0, pnum=(1, 2, 1), fnum=1, title='raw') >>> kwplot.imshow(final1, pnum=(1, 2, 2), fnum=1, title='optimized')
- property num_overviews¶
Returns: int
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedStack(parts, axis)[source]¶
Bases:
DelayedNaryOperationStacks multiple arrays together.
- property shape¶
Returns: None | Tuple[int | None, …]
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedUnaryOperation(subdata)[source]¶
Bases:
DelayedOperationFor operations that have a single input array
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.DelayedWarp(subdata, transform, dsize='auto', antialias=True, interpolation='linear', border_value='auto', noop_eps=0)[source]¶
Bases:
DelayedImageApplies an affine transform to an image.
Example
>>> from delayed_image.delayed_nodes import * # NOQA >>> from delayed_image import DelayedLoad >>> self = DelayedLoad.demo(dsize=(16, 16)).prepare() >>> warp1 = self.warp({'scale': 3}) >>> warp2 = warp1.warp({'theta': 0.1}) >>> warp3 = warp2._opt_fuse_warps() >>> warp3._validate() >>> print(ub.repr2(warp2.nesting(), nl=-1, sort=0)) >>> print(ub.repr2(warp3.nesting(), nl=-1, sort=0))
- property transform¶
Returns: kwimage.Affine
- optimize()[source]¶
- Returns
DelayedImage
Example
>>> # Demo optimization that removes a noop warp >>> from delayed_image import DelayedLoad >>> import kwimage >>> base = DelayedLoad.demo(channels='r|g|b').prepare() >>> self = base.warp(kwimage.Affine.eye()) >>> new = self.optimize() >>> assert len(self.as_graph().nodes) == 2 >>> assert len(new.as_graph().nodes) == 1
Example
>>> # Test optimize nans >>> from delayed_image import DelayedNans >>> import kwimage >>> base = DelayedNans(dsize=(100, 100), channels='a|b|c') >>> self = base.warp(kwimage.Affine.scale(0.1)) >>> # Should simply return a new nan generator >>> new = self.optimize() >>> assert len(new.as_graph().nodes) == 1
Example
>>> # Test optimize nans >>> from delayed_image import DelayedLoad >>> import kwimage >>> base = DelayedLoad.demo(channels='r|g|b').prepare() >>> transform = kwimage.Affine.scale(1.0 + 1e-7) >>> self = base.warp(transform, dsize=base.dsize) >>> # An optimize will not remove a warp if there is any >>> # doubt if it is the identity. >>> new = self.optimize() >>> assert len(self.as_graph().nodes) == 2 >>> assert len(new.as_graph().nodes) == 2 >>> # But we can specify a threshold where it will >>> self._set_nested_params(noop_eps=1e-6) >>> new = self.optimize() >>> assert len(self.as_graph().nodes) == 2 >>> assert len(new.as_graph().nodes) == 1
- class kwcoco.util.delayed_ops.ImageOpsMixin[source]¶
Bases:
object- crop(space_slice=None, chan_idxs=None, clip=True, wrap=True, pad=0)[source]¶
Crops an image along integer pixel coordinates.
- Parameters
space_slice (Tuple[slice, slice]) – y-slice and x-slice.
chan_idxs (List[int]) – indexes of bands to take
clip (bool) – if True, the slice is interpreted normally, where it won’t go past the image extent, otherwise slicing into negative regions or past the image bounds will result in padding. Defaults to True.
wrap (bool) – if True, negative indexes “wrap around”, otherwise they are treated as is. Defaults to True.
pad (int | List[Tuple[int, int]]) – if specified, applies extra padding
- Returns
DelayedImage
Example
>>> from delayed_image import DelayedLoad >>> import kwimage >>> self = DelayedLoad.demo().prepare() >>> self = self.dequantize({'quant_max': 255}) >>> self = self.warp({'scale': 1 / 2}) >>> pad = 0 >>> h, w = space_dims = self.dsize[::-1] >>> grid = list(ub.named_product({ >>> 'left': [0, -64], 'right': [0, 64], >>> 'top': [0, -64], 'bot': [0, 64],})) >>> grid += [ >>> {'left': 64, 'right': -64, 'top': 0, 'bot': 0}, >>> {'left': 64, 'right': 64, 'top': 0, 'bot': 0}, >>> {'left': 0, 'right': 0, 'top': 64, 'bot': -64}, >>> {'left': 64, 'right': -64, 'top': 64, 'bot': -64}, >>> ] >>> crops = [] >>> for pads in grid: >>> space_slice = (slice(pads['top'], h + pads['bot']), >>> slice(pads['left'], w + pads['right'])) >>> delayed = self.crop(space_slice) >>> crop = delayed.finalize() >>> yyxx = kwimage.Boxes.from_slice(space_slice, wrap=False, clip=0).toformat('_yyxx').data[0] >>> title = '[{}:{}, {}:{}]'.format(*yyxx) >>> crop_canvas = kwimage.draw_header_text(crop, title, fit=True, bg_color='kw_darkgray') >>> crops.append(crop_canvas) >>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(--show) >>> import kwplot >>> kwplot.autompl() >>> canvas = kwimage.stack_images_grid(crops, pad=16, bg_value='kw_darkgreen') >>> canvas = kwimage.fill_nans_with_checkers(canvas) >>> kwplot.imshow(canvas, title='Normal Slicing: Cropped Images With Wrap+Clipped Slices', doclf=1, fnum=1) >>> kwplot.show_if_requested()

Example
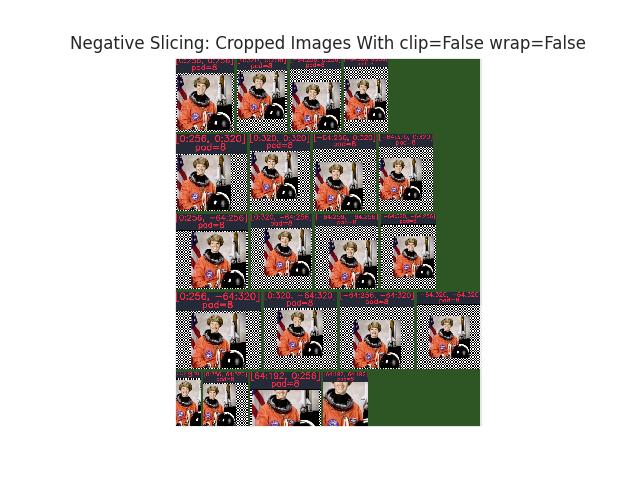
>>> # Demo the case with pads / no-clips / no-wraps >>> from delayed_image import DelayedLoad >>> import kwimage >>> self = DelayedLoad.demo().prepare() >>> self = self.dequantize({'quant_max': 255}) >>> self = self.warp({'scale': 1 / 2}) >>> pad = [(64, 128), (32, 96)] >>> pad = [(0, 20), (0, 0)] >>> pad = 0 >>> pad = 8 >>> h, w = space_dims = self.dsize[::-1] >>> grid = list(ub.named_product({ >>> 'left': [0, -64], 'right': [0, 64], >>> 'top': [0, -64], 'bot': [0, 64],})) >>> grid += [ >>> {'left': 64, 'right': -64, 'top': 0, 'bot': 0}, >>> {'left': 64, 'right': 64, 'top': 0, 'bot': 0}, >>> {'left': 0, 'right': 0, 'top': 64, 'bot': -64}, >>> {'left': 64, 'right': -64, 'top': 64, 'bot': -64}, >>> ] >>> crops = [] >>> for pads in grid: >>> space_slice = (slice(pads['top'], h + pads['bot']), >>> slice(pads['left'], w + pads['right'])) >>> delayed = self._padded_crop(space_slice, pad=pad) >>> crop = delayed.finalize(optimize=1) >>> yyxx = kwimage.Boxes.from_slice(space_slice, wrap=False, clip=0).toformat('_yyxx').data[0] >>> title = '[{}:{}, {}:{}]'.format(*yyxx) >>> if pad: >>> title += f'{chr(10)}pad={pad}' >>> crop_canvas = kwimage.draw_header_text(crop, title, fit=True, bg_color='kw_darkgray') >>> crops.append(crop_canvas) >>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(--show) >>> import kwplot >>> kwplot.autompl() >>> canvas = kwimage.stack_images_grid(crops, pad=16, bg_value='kw_darkgreen', resize='smaller') >>> canvas = kwimage.fill_nans_with_checkers(canvas) >>> kwplot.imshow(canvas, title='Negative Slicing: Cropped Images With clip=False wrap=False', doclf=1, fnum=2) >>> kwplot.show_if_requested()
- warp(transform, dsize='auto', **warp_kwargs)[source]¶
Applys an affine transformation to the image. See
DelayedWarp.- Parameters
transform (ndarray | dict | kwimage.Affine) – a coercable affine matrix. See
kwimage.Affinefor details on what can be coerced.dsize (Tuple[int, int] | str) – The width / height of the output canvas. If ‘auto’, dsize is computed such that the positive coordinates of the warped image will fit in the new canvas. In this case, any pixel that maps to a negative coordinate will be clipped. This has the property that the input transformation is not modified.
antialias (bool) – if True determines if the transform is downsampling and applies antialiasing via gaussian a blur. Defaults to False
interpolation (str) – interpolation code or cv2 integer. Interpolation codes are linear, nearest, cubic, lancsoz, and area. Defaults to “linear”.
border_value (int | float | str) – if auto will be nan for float and 0 for int.
noop_eps (float) – This is the tolerance for optimizing a warp away. If the transform has all of its decomposed parameters (i.e. scale, rotation, translation, shear) less than this value, the warp node can be optimized away. Defaults to 0.
- Returns
DelayedImage
- dequantize(quantization)[source]¶
Rescales image intensities from int to floats.
- Parameters
quantization (Dict[str, Any]) – see
delayed_image.helpers.dequantize()- Returns
DelayedDequantize
- get_overview(overview)[source]¶
Downsamples an image by a factor of two.
- Parameters
overview (int) – the overview to use (assuming it exists)
- Returns
DelayedOverview
- get_transform_from(src)[source]¶
Find a transform from a given node (src) to this node (self / dst).
Given two delayed images src and dst that share a common leaf, find the transform from src to dst.
- Parameters
src (DelayedOperation) – the other view to get a transform to. This must share a leaf with self (which is the dst).
- Returns
The transform that warps the space of src to the space of self.
- Return type
Example
>>> from delayed_image import * # NOQA >>> from delayed_image.delayed_leafs import DelayedLoad >>> base = DelayedLoad.demo().prepare() >>> src = base.scale(2) >>> dst = src.warp({'scale': 4, 'offset': (3, 5)}) >>> transform = dst.get_transform_from(src) >>> tf = transform.decompose() >>> assert tf['scale'] == (4, 4) >>> assert tf['offset'] == (3, 5)
Example
>>> from delayed_image import demo >>> self = demo.non_aligned_leafs() >>> leaf = list(self._leaf_paths())[0][0] >>> tf1 = self.get_transform_from(leaf) >>> tf2 = leaf.get_transform_from(self) >>> np.allclose(np.linalg.inv(tf2), tf1)