kwcoco.coco_image module¶
Defines the CocoImage class which is an object oriented way of manipulating data pointed to by a COCO image dictionary.
Notably this provides the .imdelay method for delayed image loading ( which
enables things like fast loading of subimage-regions / coarser scales in images
that contain tiles / overviews - e.g. Cloud Optimized Geotiffs or COGs (Medical
image formats may be supported in the future).
- class kwcoco.coco_image.CocoImage(img, dset=None)[source]¶
Bases:
AliasedDictProxy,NiceReprAn object-oriented representation of a coco image.
It provides helper methods that are specific to a single image.
This operates directly on a single coco image dictionary, but it can optionally be connected to a parent dataset, which allows it to use CocoDataset methods to query about relationships and resolve pointers.
This is different than the Images class in coco_object1d, which is just a vectorized interface to multiple objects.
Example
>>> import kwcoco >>> dset1 = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo('shapes8') >>> dset2 = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo('vidshapes8-multispectral')
>>> self = kwcoco.CocoImage(dset1.imgs[1], dset1) >>> print('self = {!r}'.format(self)) >>> print('self.channels = {}'.format(ub.urepr(self.channels, nl=1)))
>>> self = kwcoco.CocoImage(dset2.imgs[1], dset2) >>> print('self.channels = {}'.format(ub.urepr(self.channels, nl=1))) >>> self.primary_asset() >>> assert 'auxiliary' in self
- property bundle_dpath¶
- property video¶
Helper to grab the video for this image if it exists
- detach()[source]¶
Removes references to the underlying coco dataset, but keeps special information such that it wont be needed.
- property assets¶
- property datetime¶
Try to get datetime information for this image. Not always possible.
- property channels¶
- property num_channels¶
- property dsize¶
- primary_asset(requires=None)[source]¶
Compute a “main” image asset.
Notes
Uses a heuristic.
First, try to find the auxiliary image that has with the smallest
distortion to the base image (if known via warp_aux_to_img)
Second, break ties by using the largest image if w / h is known
Last, if previous information not available use the first auxiliary image.
- Parameters
requires (List[str] | None) – list of attribute that must be non-None to consider an object as the primary one.
- Returns
the asset dict or None if it is not found
- Return type
None | dict
Todo
[ ] Add in primary heuristics
Example
>>> import kwarray >>> from kwcoco.coco_image import * # NOQA >>> rng = kwarray.ensure_rng(0) >>> def random_auxiliary(name, w=None, h=None): >>> return {'file_name': name, 'width': w, 'height': h} >>> self = CocoImage({ >>> 'auxiliary': [ >>> random_auxiliary('1'), >>> random_auxiliary('2'), >>> random_auxiliary('3'), >>> ] >>> }) >>> assert self.primary_asset()['file_name'] == '1' >>> self = CocoImage({ >>> 'auxiliary': [ >>> random_auxiliary('1'), >>> random_auxiliary('2', 3, 3), >>> random_auxiliary('3'), >>> ] >>> }) >>> assert self.primary_asset()['file_name'] == '2'
- iter_image_filepaths(with_bundle=True)[source]¶
Could rename to iter_asset_filepaths
- Parameters
with_bundle (bool) – If True, prepends the bundle dpath to fully specify the path. Otherwise, just returns the registered string in the file_name attribute of each asset. Defaults to True.
- Yields
ub.Path
- iter_asset_objs()[source]¶
Iterate through base + auxiliary dicts that have file paths
- Yields
dict – an image or auxiliary dictionary
- find_asset_obj(channels)[source]¶
Find the asset dictionary with the specified channels
Example
>>> import kwcoco >>> coco_img = kwcoco.CocoImage({'width': 128, 'height': 128}) >>> coco_img.add_auxiliary_item( >>> 'rgb.png', channels='red|green|blue', width=32, height=32) >>> assert coco_img.find_asset_obj('red') is not None >>> assert coco_img.find_asset_obj('green') is not None >>> assert coco_img.find_asset_obj('blue') is not None >>> assert coco_img.find_asset_obj('red|blue') is not None >>> assert coco_img.find_asset_obj('red|green|blue') is not None >>> assert coco_img.find_asset_obj('red|green|blue') is not None >>> assert coco_img.find_asset_obj('black') is None >>> assert coco_img.find_asset_obj('r') is None
Example
>>> # Test with concise channel code >>> import kwcoco >>> coco_img = kwcoco.CocoImage({'width': 128, 'height': 128}) >>> coco_img.add_auxiliary_item( >>> 'msi.png', channels='foo.0:128', width=32, height=32) >>> assert coco_img.find_asset_obj('foo') is None >>> assert coco_img.find_asset_obj('foo.3') is not None >>> assert coco_img.find_asset_obj('foo.3:5') is not None >>> assert coco_img.find_asset_obj('foo.3000') is None
- add_annotation(**ann)[source]¶
Adds an annotation to this image.
This is a convinience method, and requires that this CocoImage is still connected to a parent dataset.
- Parameters
**ann – annotation attributes (e.g. bbox, category_id)
- Returns
the new annotation id
- Return type
- SeeAlso:
kwcoco.CocoDataset.add_annotation()
- add_asset(file_name=None, channels=None, imdata=None, warp_aux_to_img=None, width=None, height=None, imwrite=False)[source]¶
Adds an auxiliary / asset item to the image dictionary.
This operation can be done purely in-memory (the default), or the image data can be written to a file on disk (via the imwrite=True flag).
- Parameters
file_name (str | PathLike | None) – The name of the file relative to the bundle directory. If unspecified, imdata must be given.
channels (str | kwcoco.FusedChannelSpec | None) – The channel code indicating what each of the bands represents. These channels should be disjoint wrt to the existing data in this image (this is not checked).
imdata (ndarray | None) – The underlying image data this auxiliary item represents. If unspecified, it is assumed file_name points to a path on disk that will eventually exist. If imdata, file_name, and the special imwrite=True flag are specified, this function will write the data to disk.
warp_aux_to_img (kwimage.Affine | None) – The transformation from this auxiliary space to image space. If unspecified, assumes this item is related to image space by only a scale factor.
width (int | None) – Width of the data in auxiliary space (inferred if unspecified)
height (int | None) – Height of the data in auxiliary space (inferred if unspecified)
imwrite (bool) – If specified, both imdata and file_name must be specified, and this will write the data to disk. Note: it it recommended that you simply call imwrite yourself before or after calling this function. This lets you better control imwrite parameters.
Todo
[ ] Allow imwrite to specify an executor that is used to
return a Future so the imwrite call does not block.
Example
>>> from kwcoco.coco_image import * # NOQA >>> import kwcoco >>> dset = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo('vidshapes8-multispectral') >>> coco_img = dset.coco_image(1) >>> imdata = np.random.rand(32, 32, 5) >>> channels = kwcoco.FusedChannelSpec.coerce('Aux:5') >>> coco_img.add_asset(imdata=imdata, channels=channels)
Example
>>> import kwcoco >>> dset = kwcoco.CocoDataset() >>> gid = dset.add_image(name='my_image_name', width=200, height=200) >>> coco_img = dset.coco_image(gid) >>> coco_img.add_asset('path/img1_B0.tif', channels='B0', width=200, height=200) >>> coco_img.add_asset('path/img1_B1.tif', channels='B1', width=200, height=200) >>> coco_img.add_asset('path/img1_B2.tif', channels='B2', width=200, height=200) >>> coco_img.add_asset('path/img1_TCI.tif', channels='r|g|b', width=200, height=200)
- imdelay(channels=None, space='image', resolution=None, bundle_dpath=None, interpolation='linear', antialias=True, nodata_method=None, RESOLUTION_KEY=None)[source]¶
Perform a delayed load on the data in this image.
The delayed load can load a subset of channels, and perform lazy warping operations. If the underlying data is in a tiled format this can reduce the amount of disk IO needed to read the data if only a small crop or lower resolution view of the data is needed.
Note
This method is experimental and relies on the delayed load proof-of-concept.
- Parameters
gid (int) – image id to load
channels (kwcoco.FusedChannelSpec) – specific channels to load. if unspecified, all channels are loaded.
space (str) – can either be “image” for loading in image space, or “video” for loading in video space.
resolution (None | str | float) – If specified, applies an additional scale factor to the result such that the data is loaded at this specified resolution. This requires that the image / video has a registered resolution attribute and that its units agree with this request.
Todo
- [ ] This function could stand to have a better name. Maybe imread
with a delayed=True flag? Or maybe just delayed_load?
Example
>>> from kwcoco.coco_image import * # NOQA >>> import kwcoco >>> gid = 1 >>> # >>> dset = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo('vidshapes8-multispectral') >>> self = CocoImage(dset.imgs[gid], dset) >>> delayed = self.imdelay() >>> print('delayed = {!r}'.format(delayed)) >>> print('delayed.finalize() = {!r}'.format(delayed.finalize())) >>> print('delayed.finalize() = {!r}'.format(delayed.finalize())) >>> # >>> dset = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo('shapes8') >>> delayed = dset.coco_image(gid).imdelay() >>> print('delayed = {!r}'.format(delayed)) >>> print('delayed.finalize() = {!r}'.format(delayed.finalize())) >>> print('delayed.finalize() = {!r}'.format(delayed.finalize()))
>>> crop = delayed.crop((slice(0, 3), slice(0, 3))) >>> crop.finalize()
>>> # TODO: should only select the "red" channel >>> dset = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo('shapes8') >>> delayed = CocoImage(dset.imgs[gid], dset).imdelay(channels='r')
>>> import kwcoco >>> gid = 1 >>> # >>> dset = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo('vidshapes8-multispectral') >>> delayed = dset.coco_image(gid).imdelay(channels='B1|B2', space='image') >>> print('delayed = {!r}'.format(delayed)) >>> print('delayed.finalize() = {!r}'.format(delayed.finalize())) >>> delayed = dset.coco_image(gid).imdelay(channels='B1|B2|B11', space='image') >>> print('delayed = {!r}'.format(delayed)) >>> print('delayed.finalize() = {!r}'.format(delayed.finalize())) >>> delayed = dset.coco_image(gid).imdelay(channels='B8|B1', space='video') >>> print('delayed = {!r}'.format(delayed)) >>> print('delayed.finalize() = {!r}'.format(delayed.finalize()))
>>> delayed = dset.coco_image(gid).imdelay(channels='B8|foo|bar|B1', space='video') >>> print('delayed = {!r}'.format(delayed)) >>> print('delayed.finalize() = {!r}'.format(delayed.finalize()))
Example
>>> import kwcoco >>> dset = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo() >>> coco_img = dset.coco_image(1) >>> # Test case where nothing is registered in the dataset >>> delayed = coco_img.imdelay() >>> final = delayed.finalize() >>> assert final.shape == (512, 512, 3)
>>> delayed = coco_img.imdelay() >>> final = delayed.finalize() >>> print('final.shape = {}'.format(ub.urepr(final.shape, nl=1))) >>> assert final.shape == (512, 512, 3)
Example
>>> # Test that delay works when imdata is stored in the image >>> # dictionary itself. >>> from kwcoco.coco_image import * # NOQA >>> import kwcoco >>> dset = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo('vidshapes8-multispectral') >>> coco_img = dset.coco_image(1) >>> imdata = np.random.rand(6, 6, 5) >>> imdata[:] = np.arange(5)[None, None, :] >>> channels = kwcoco.FusedChannelSpec.coerce('Aux:5') >>> coco_img.add_auxiliary_item(imdata=imdata, channels=channels) >>> delayed = coco_img.imdelay(channels='B1|Aux:2:4') >>> final = delayed.finalize()
Example
>>> # Test delay when loading in asset space >>> from kwcoco.coco_image import * # NOQA >>> import kwcoco >>> dset = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo('vidshapes8-msi-multisensor') >>> coco_img = dset.coco_image(1) >>> stream1 = coco_img.channels.streams()[0] >>> stream2 = coco_img.channels.streams()[1] >>> asset_delayed = coco_img.imdelay(stream1, space='asset') >>> img_delayed = coco_img.imdelay(stream1, space='image') >>> vid_delayed = coco_img.imdelay(stream1, space='video') >>> # >>> aux_imdata = asset_delayed.as_xarray().finalize() >>> img_imdata = img_delayed.as_xarray().finalize() >>> assert aux_imdata.shape != img_imdata.shape >>> # Cannot load multiple asset items at the same time in >>> # asset space >>> import pytest >>> fused_channels = stream1 | stream2 >>> from delayed_image.delayed_nodes import CoordinateCompatibilityError >>> with pytest.raises(CoordinateCompatibilityError): >>> aux_delayed2 = coco_img.imdelay(fused_channels, space='asset')
Example
>>> # Test loading at a specific resolution. >>> from kwcoco.coco_image import * # NOQA >>> import kwcoco >>> dset = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo('vidshapes8-msi-multisensor') >>> coco_img = dset.coco_image(1) >>> coco_img.img['resolution'] = '1 meter' >>> img_delayed1 = coco_img.imdelay(space='image') >>> vid_delayed1 = coco_img.imdelay(space='video') >>> # test with unitless request >>> img_delayed2 = coco_img.imdelay(space='image', resolution=3.1) >>> vid_delayed2 = coco_img.imdelay(space='video', resolution='3.1 meter') >>> np.ceil(img_delayed1.shape[0] / 3.1) == img_delayed2.shape[0] >>> np.ceil(vid_delayed1.shape[0] / 3.1) == vid_delayed2.shape[0] >>> # test with unitless data >>> coco_img.img['resolution'] = 1 >>> img_delayed2 = coco_img.imdelay(space='image', resolution=3.1) >>> vid_delayed2 = coco_img.imdelay(space='video', resolution='3.1 meter') >>> np.ceil(img_delayed1.shape[0] / 3.1) == img_delayed2.shape[0] >>> np.ceil(vid_delayed1.shape[0] / 3.1) == vid_delayed2.shape[0]
- valid_region(space='image')[source]¶
If this image has a valid polygon, return it in image, or video space
- property warp_vid_from_img¶
Affine transformation that warps image space -> video space.
- property warp_img_from_vid¶
Affine transformation that warps video space -> image space.
- resolution(space='image', channel=None, RESOLUTION_KEY=None)[source]¶
Returns the resolution of this CocoImage in the requested space if known. Errors if this information is not registered.
- Parameters
space (str) – the space to the resolution of. Can be either “image”, “video”, or “asset”.
channel (str | kwcoco.FusedChannelSpec | None) – a channel that identifies a single asset, only relevant if asking for asset space
- Returns
has items mag (with the magnitude of the resolution) and unit, which is a convinience and only loosely enforced.
- Return type
Dict
Example
>>> import kwcoco >>> dset = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo('vidshapes8-multispectral') >>> self = dset.coco_image(1) >>> self.img['resolution'] = 1 >>> self.resolution() >>> self.img['resolution'] = '1 meter' >>> self.resolution(space='video') {'mag': (1.0, 1.0), 'unit': 'meter'} >>> self.resolution(space='asset', channel='B11') >>> self.resolution(space='asset', channel='B1')
- add_auxiliary_item(**kwargs)¶
- delay(**kwargs)¶
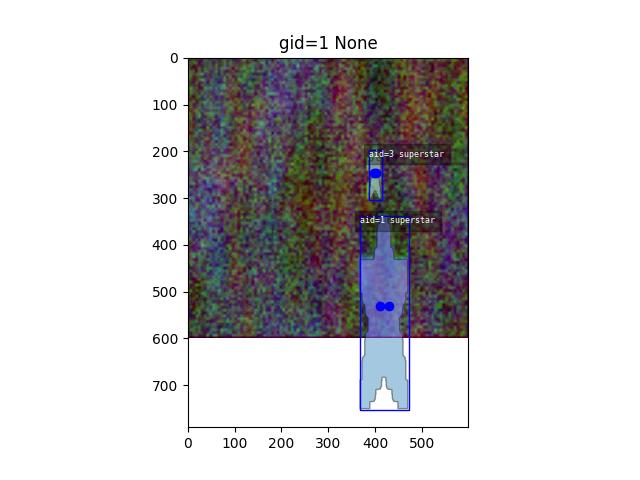
- show(**kwargs)[source]¶
Show the image with matplotlib if possible
- SeeAlso:
kwcoco.CocoDataset.show_image()
Example
>>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(module:kwplot) >>> import kwcoco >>> dset = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo('vidshapes8-multispectral') >>> self = dset.coco_image(1) >>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(--show) >>> import kwplot >>> kwplot.autoplt() >>> self.show()
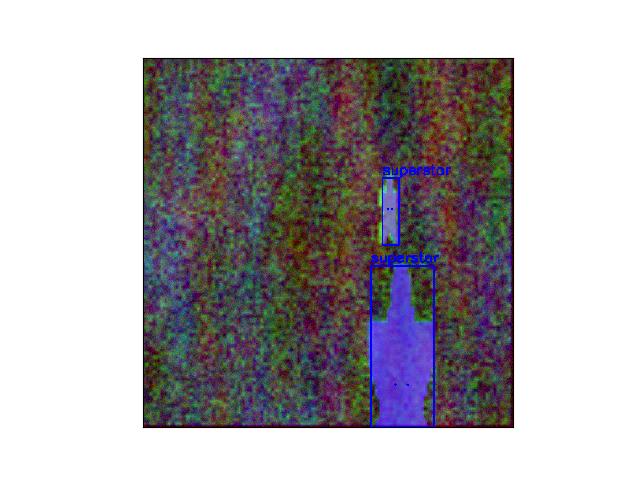
- draw(**kwargs)[source]¶
Draw the image on an ndarray using opencv
- SeeAlso:
kwcoco.CocoDataset.draw_image()
Example
>>> import kwcoco >>> dset = kwcoco.CocoDataset.demo('vidshapes8-multispectral') >>> self = dset.coco_image(1) >>> canvas = self.draw() >>> # xdoctest: +REQUIRES(--show) >>> import kwplot >>> kwplot.autompl() >>> kwplot.imshow(canvas)
- class kwcoco.coco_image.CocoAsset(asset)[source]¶
Bases:
AliasedDictProxy,NiceReprA Coco Asset / Auxiliary Item
Represents one 2D image file relative to a parent img.
Could be a single asset, or an image with sub-assets, but sub-assets are ignored here.
Initially we called these “auxiliary” items, but I think we should change their name to “assets”, which better maps with STAC terminology.
Example
>>> from kwcoco.coco_image import * # NOQA >>> self = CocoAsset({'warp_aux_to_img': 'foo'}) >>> assert 'warp_aux_to_img' in self >>> assert 'warp_img_from_asset' in self >>> assert 'warp_wld_from_asset' not in self >>> assert 'warp_to_wld' not in self >>> self['warp_aux_to_img'] = 'bar' >>> assert self._proxy == {'warp_aux_to_img': 'bar'}